Table of Contents
ToggleUbuntu, a widely-used distribution of the Linux operating system, provides a conducive environment for software development. For budding developers or those new to the Linux ecosystem, compiling a C program might seem daunting. This article aims to demystify the process, offering a step-by-step guide to compiling and running C programs in Ubuntu.
Detailed Steps to Compile a C Program in Ubuntu
Steps to compile a C program In Ubuntu are:
Writing Your First C Program
- Let’s begin by writing simple C program in a text editor of your choice.
- Save the file with a
.cextension to desired location, e.g.,hello.c.
// Simple Hello World Program In C
#include <stdio.h> // Include the standard input/output library.
int main() {
// This is the main function, where program execution starts.
// Print a message to the console.
printf("Hello, World!\n"); // The '\n' represents a newline character.
// Return 0 to indicate successful execution to the operating system.
return 0;
}Checking if GCC is Installed
- Before compiling, it’s crucial to ensure you have the GCC compiler.
- In the terminal, type:
gcc --version- If GCC is installed, this command will display its version.
- If not, you’ll need to install it.


A C compiler is a vital tool in software development, responsible for translating human-readable C source code into machine-readable binary code. It not only detects syntax and semantic errors but also optimises code to enhance efficiency and performance, resulting in faster and more reliable software execution.562CD9
Installing the GCC Compiler (if not installed)
- Use the command to install GCC using APT package manager:
sudo apt install gcc- This installs the GNU Compiler Collection, which includes the C compiler.
Generating Object File
- Compilation translates the human-readable C code into machine code. So for this, we will use the GCC compiler installed above.
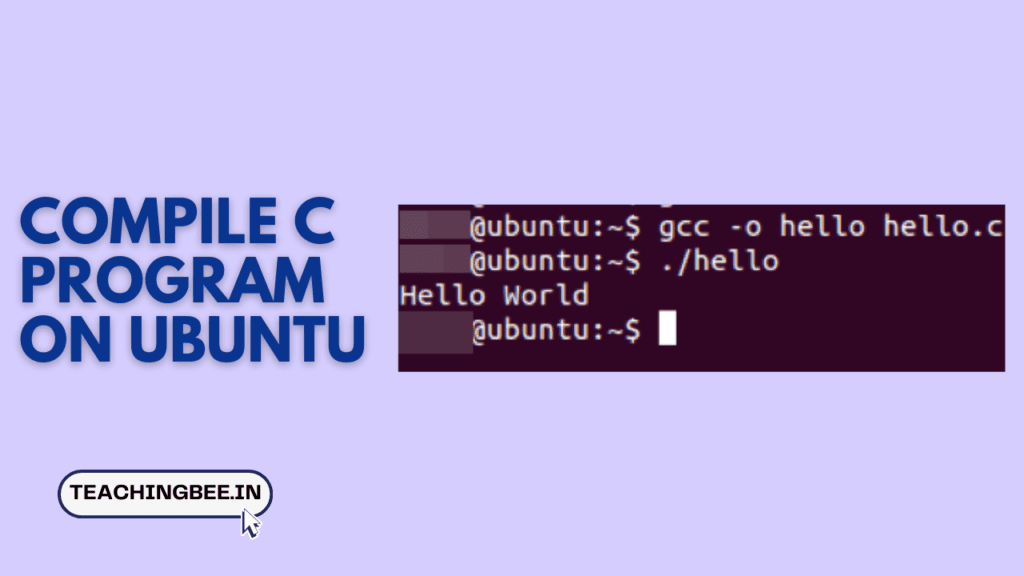
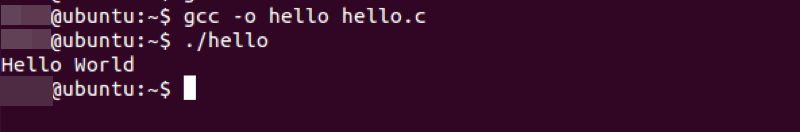
- The command compiles the
hello.cfile. The-oflag specifies the output file, which in this case is named hello. If no file name is specified for object file, by default object file is created by name a.out.
gcc -o hello hello.c- This process generates an object file in the current folder, which is a binary file that can be executed.
Note: In the above command, you need to specify the path to locate a .c file if it is located in a different directory.
Storing the Object File in a Different Location
- Alternatively, you can specify a path along with the name to determine where the compiled object file will be stored.
- For example, if you want to store the object file in a directory named
bin, you can use:
gcc -o bin/hello hello.c- This will compile
hello.cand store the resulting object filehelloin thebindirectory. - Ensure the directory exists before compiling, or you’ll receive an error. If it doesn’t exist, you can create it using the command
mkdir bin.
Running the Compiled Program
- Post compilation, you can run the program using:
./hello- The
./prefix indicates that the executable is in the current directory.

Running the Object File from a Different Location
- If you’ve stored the object file in a different directory, you’ll need to navigate to that directory or specify its path when running the file.
- For the above example, from the main directory, you can run the program using:
./bin/helloKey Takeaways
- GCC compiler needs to be installed to compile C programs on Ubuntu. The command
gcc --versionchecks if it’s installed. - To compile a C program ‘hello.c’, use
gcc -o hello hello.c. This generates an executable object file named ‘hello’. - The
-oflag in the GCC command specifies the output file name for the compiled program. - To run the compiled program, use
./helloif the object file is in the current directory. Use a path like./bin/helloif the object file is stored elsewhere. - Compilation converts human-readable C code to machine code (object file) that can then be executed on the OS.
Checkout more similar blogs
Download Code Blocks for macOS
Download Code Blocks for Windows 10&11
Download Turbo C Compiler on Windows
Checkout more C Tutorials here.
I hope You liked the post ?. For more such posts, ? subscribe to our newsletter. Try out our free resume checker service where our Industry Experts will help you by providing resume score based on the key criteria that recruiters and hiring managers are looking for.
FAQs
Why do we need the GCC compiler?
Answer: GCC translates C code into machine code, making it executable. Without it, the system wouldn’t understand the program.
What happens if I don’t use the -o flag during compilation?
Answer: If omitted, GCC will generate an output file named a.out by default. However, specifying a name with -o makes it easier to identify and manage your programs.
Why is the ./ prefix used before running the executable?
Answer: In Linux, ./ refers to the current directory. It tells the system to look for the executable in the directory you’re currently in.