Table of Contents
ToggleIn this blog post, we will see how to write C program to calculate factorial of a number using recursion with detailed explanation.
Before we start let’s understand few basic.
What is factorial of a number?
The factorial of a non-negative integer, denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers up to that number. In other words, it’s the multiplication of all the natural numbers from 1 to n.
Mathematically, the factorial is defined as:
n!= n×(n−1)×(n−2)×…×3×2×1
For example:
Example: Let’s find the factorial of 5, denoted as 5!5!.
5!=5×4×3×2×1=1205!=5×4×3×2×1=120
So, the factorial of 5 is 120. The factorial function is commonly used in mathematics and programming, especially in the context of permutations, combinations, and probability calculations. It grows rapidly as the input value increases, demonstrating its exponential nature.
To write a C Program to Calculate Factorial Of A Number Using Recursion you can follow this algorithm and corresponding pseudo code.
Algorithm:
- Function Definition:
- Define a function
factorialthat takes an integernas its parameter.
- Define a function
- Base Case Check:
- Check if
nis equal to 0 or 1.- If true, return 1 (since the factorial of 0 and 1 is 1).
- Check if
- Recursive Case:
- If
nis greater than 1, recursively call thefactorialfunction with the argumentn - 1.- The result of the recursive call represents the factorial of
n - 1.
- The result of the recursive call represents the factorial of
- If
- Multiply and Return:
- Multiply the result of the recursive call by
n. - Return the product as the final result.
- Multiply the result of the recursive call by
Recursive Relation
f(n) = n*f(n-1)
C Program To Calculate Factorial Of A Number Using Recursion
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate factorial using recursion
int factorial(int n) {
// Base case: factorial of 0 and 1 is 1
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
// Recursive case: n! = n * (n-1)!
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
int main() {
// Example: Calculate factorial of 5
int number = 5;
int result = factorial(number);
printf("Factorial of %d is: %d\n", number, result);
return 0;
}
Output
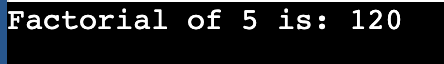
In the above program,
The factorial function is defined to calculate the factorial of a given number using recursion. The base case checks if the input is 0 or 1, and if so, returns 1. Otherwise, it recursively calls itself with the argument n - 1 until reaching the base case. The final result is the product of the current n and the result of the recursive call. The program then calculates and prints the factorial of 5 as an example..
The execution flow for the input value as 5 would unfold as follows:
Main Function:
- Call the
factorialfunction with5as an argument.
Factorial Function (n = 5):
- Check if
nis 0 or 1 (Base case not met, as n = 5). - Recursively call
factorialwithn - 1(4).
Factorial Function (n = 4):
- Check if
nis 0 or 1 (Base case not met, as n = 4). - Recursively call
factorialwithn - 1(3).
Factorial Function (n = 3):
- Check if
nis 0 or 1 (Base case not met, as n = 3). - Recursively call
factorialwithn - 1(2).
Factorial Function (n = 2):
- Check if
nis 0 or 1 (Base case not met, as n = 2). - Recursively call
factorialwithn - 1(1).
Factorial Function (n = 1):
- Check if
nis 0 or 1 (Base case met, return 1).
Backtracking:
- The recursive call for n = 1 returns 1.
- Multiply the result (1) by the current
n(2) in the n = 2 frame, returning 2. - Multiply the result (2) by the current
n(3) in the n = 3 frame, returning 6. - Multiply the result (6) by the current
n(4) in the n = 4 frame, returning 24. - Multiply the result (24) by the current
n(5) in the n = 5 frame, returning 120.
So, the factorial of 5 is calculated as 120 using recursion in the provided C program.
If you liked this post you can checkout other C Programs.
FAQ
What is the factorial of 0?
The factorial of 0, denoted as 0!, is defined to be 1. It serves as the base case in the factorial function.
What happens if I try to calculate the factorial of a negative number?
Factorial is not defined for negative integers. Attempting to calculate the factorial of a negative number is undefined and typically results in an error. Factorial is only valid for non-negative integers.


