Table of Contents
ToggleProblem Statement
Given a Binary Tree, print left view of binary tree. Left view of Binary Tree is set of nodes visible when tree is visited from left side.
Example:
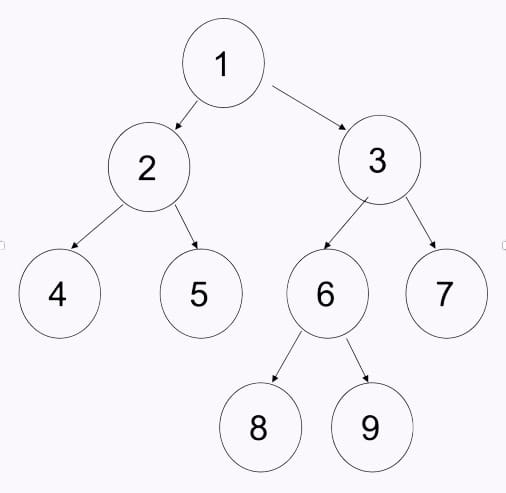

Output: 1 2 4 8
Problem Explanation
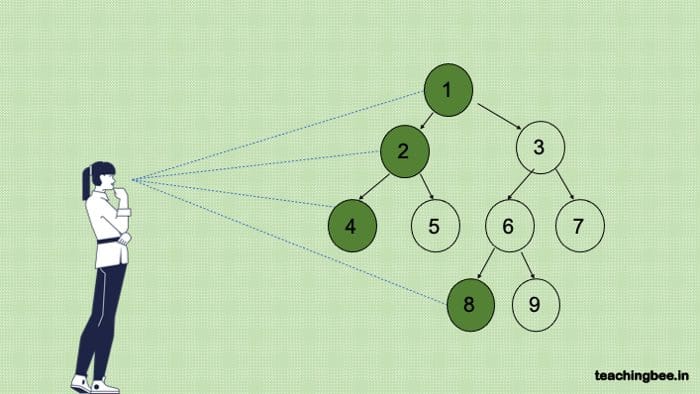

First, let’s understand what exactly is the left side of binary tree? Take a look at the image above and the person can see the nodes that are on the left side of the tree. In simpler terms I could say that it is the first element of each one of the layers.
Level 0: 1 Level 1: 2 Level 2: 4. Level 3: 8
Left View Of Binary Tree Solution
Method 1: Recursion
The problem can be solved with a simple preorder traversal using recursion. Idea is to keep track of the node’s level by sending a parameter to all Recursive calls. The goal is to track the highest level as well. If we come across any node with a level greater than its maximum level, we print the node since this is the first node of its level.
Algorithm:
Do a preorder the traversal in the TreeCheck if this node is first from its level by comparing max level visited so far with level of nodeIf its first node print the node and update max level visited so far to current nodeSince we want left view, we will Move to the left child first and increase your level oneMove to the right and keep increasing the level.
Implementation:
// Java program to print left view of binary tree
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class LeftViewOfBinaryTree {
//Variable to keep track of maximum level visited so far
static int maxLevelVisitedSoFar = 0;
// recursive function to print left view using preoroder
static void leftViewOfBinaryTree(Node node, int level) {
// Base Case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this is the first node of its level
if (maxLevelVisitedSoFar < level) {
System.out.print(" " + node.data);
maxLevelVisitedSoFar = level;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees incrementing the level
leftViewOfBinaryTree(node.left, level + 1);
leftViewOfBinaryTree(node.right, level + 1);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
root.right.left = new Node(7);
root.right.right.left = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
leftViewOfBinaryTree(root, 1);
}
}Time Complexity: O(n).
Auxiliary Space: O(n), due to the stack space during recursive call.
Method 2: Iterative Using Queue
In this method, we will use level order traversal to print left view of binary tree. Since our main objective is to find the left most node of every level so by using a simple level order traversal we will print the leftmost node at every level. For this, we’ll use queue to store all the nodes in the current level.
Algorithm:
Perform level order traversal.Print the first node at each level in the tree and push the children of all nodes at each level in the queue.Repeat the above steps till queue becomes empty.
Implementation:
// Java program to print left view of binary tree
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class LeftViewOfBinaryTree {
static void leftViewOfBinaryTree(Node node, int level) {
// base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Queue for level order traversal
Queue < Node > queue = new LinkedList < > ();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// Calculate number of nodes at current level
int n = queue.size();
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node temp = queue.poll();
// Print the left most/First node of the current level
if (i == 1)
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != null)
queue.add(temp.left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != null)
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
root.right.left = new Node(7);
root.right.right.left = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
leftViewOfBinaryTree(root, 1);
}
}Time Complexity: O(n).
Auxiliary Space: O(n), for maintaining queue.
Conclusion
In this post we discussed iterative and recursive way to print left view of binary tree.
Got a question or just want to chat? Comment below or drop by our forums, where a bunch of the friendliest people you’ll ever run into will be happy to help you out!