Table of Contents
ToggleIn this blog post, we will provide an overview about what are the ITIL processes and processes you should know about as an IT professional or someone looking to get into IT service management.
We will explain what each key ITIL processes entails, its objectives, and how adopting these processes can help improve IT service quality and efficiency. Whether you are completely new to ITIL or looking for a refresher, this post will provide a solid grounding in the fundamental ITIL processes that serve as the building blocks for robust IT service management.
What is ITIL?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a set of best practices and frameworks for IT service management. Here are some key things to know about ITIL:
- Provides guidelines for delivering high quality IT services aligned with business needs.
- Focuses on the entire IT service lifecycle – design, implementation, operation, improvement.
- Covers processes like incident management, problem management, change management, release management etc.
- Emphasizes comprehensive IT service management principles rather than just IT processes.
- Owned by AXELOS – a joint venture between the UK government and Capita plc.
- ITIL frameworks evolve periodically – ITIL v3, ITIL 4, ITIL 4 Foundation etc.
- ITIL certified professionals are highly sought after in ITSM roles.
- Helps improve IT service availability, continuity and optimisation.
- Widely adopted globally by organizations for IT best practices.
What are the ITIL Processes And Lifecycle?
Overview of ITIL Lifecycle
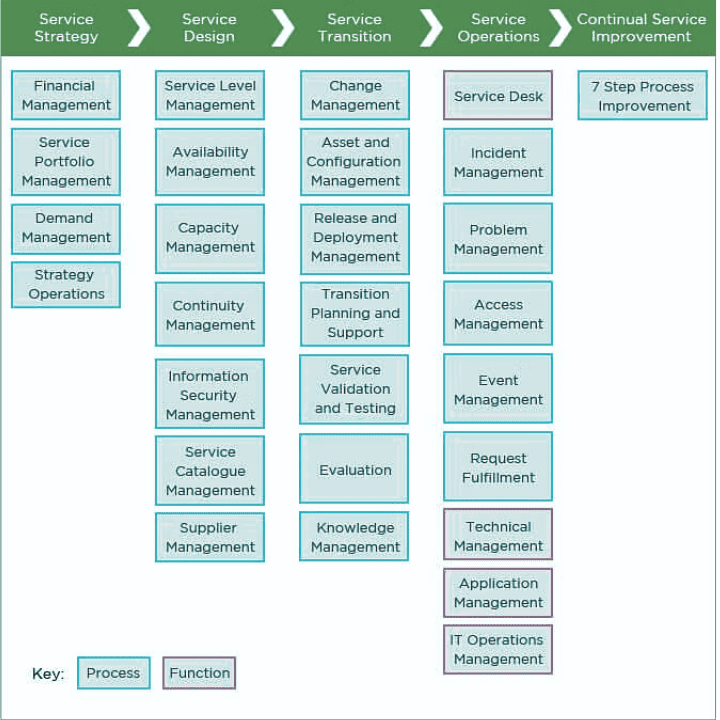
Here is an overview of the ITIL service lifecycle and key ITIL processes. The ITIL service lifecycle provides a framework for managing IT services across 5 key stages:
- Service Strategy – Strategic assessment and planning
- Service Design – Design and development of IT services and processes
- Service Transition – Provides the overall planning for service introduction, transformation, and retirement, as well as coordinating the required resources.
- Service Operation – Day to day delivery and support of IT services
- Continual Service Improvement – Ongoing improvement of services

ITIL Processes
Key ITIL Processes are:
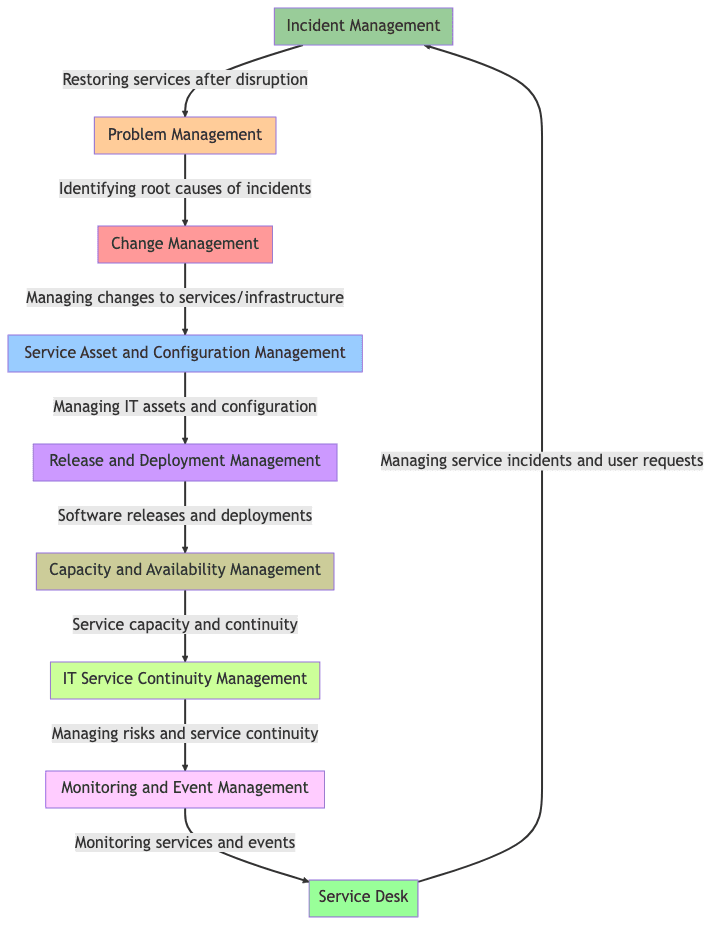
- Incident Management – Restoring services after disruption
- Problem Management – Identifying root causes of incidents
- Change Management – Managing changes to services/infrastructure
- Service Asset and Configuration Management – Managing IT assets and configuration
- Release and Deployment Management – Software releases and deployments
- Capacity and Availability Management – Service capacity and continuity
- IT Service Continuity Management – Managing risks and service continuity
- Monitoring and Event Management – Monitoring services and events
- Service Desk – Managing service incidents and user requests
These processes span the entire service lifecycle and are designed to improve quality, reduce costs, and increase efficiency of IT services.

Importance of ITIL Processes in Today’s Business Environment
Here are some key points on what ITIL is and why it’s important in Business Environment:
- ITIL provides guidelines for IT processes, tasks, and checklists to optimize IT service quality, align IT services to business requirements, and improve efficiency.
- It outlines a systematic approach to the management and delivery of IT services across the service lifecycle stages of design, transition, operation, and improvement.
- Key concepts covered include service desk, incidents, problems, configuration, change and release management, availability, capacity, continuity, and security.
- ITIL emphasizes a business-centric, customer-focused view of IT service provisioning.
- Widely adopted ITIL frameworks include ITIL v3, ITIL 4, and ITIL 4 Foundation.
- ITIL helps IT teams improve efficiency, reduce costs, enable business continuity, ensure security, and gain competitive advantage.
- With digital transformation trends, having mature IT service management based on ITIL best practices is critical for businesses to remain responsive, agile, resilient and efficient.
- ITIL skills are highly valued across roles like IT managers, operations, architects, project managers, and consultants for service delivery.
History of ITIL
Origin and Evolution Of ITIL
Here is a brief overview of the history and evolution of ITIL:
- 1980s – ITIL originated as a set of IT service management best practice guidelines developed by the UK government’s Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA).
- Early 1990s – The initial ITIL books were published documenting best practices for IT services. The original ITIL consisted of over 30 books covering service support and delivery.
- 2000 – ITIL v2 was released improving on v1. ITIL v2 consolidated the publications into 7 core books that became widely adopted.
- 2007 – ITIL v3 was released as an upgrade to v2. It was significantly expanded across 5 core publications – Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
- 2011 – ITIL v3 was refined and improved to resolve errors and inconsistencies.
- 2019 – ITIL v4 was released focusing on agile principles and integrating ITIL practices into an end-to-end operating model for IT teams.
- Today – ITIL v4 is the most current version and provides a flexible framework for managing IT services and contributing to business value delivery. ITIL is owned by AXELOS which maintains and updates the frameworks.
- Over the years, ITIL has evolved significantly from a set of books for the UK government to an expansive library of global IT service management best practices across the service lifecycle. It has become the most widely adopted framework for ITSM.
ITIL V3 vs ITIL V4
| Basis | ITIL V3 | ITIL V4 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Date | 2007 | 2019 |
| Objective | Best practice guidance for IT service management | Flexible framework for managing services |
| Approach | Process-centric | Service value chain model |
| Processes | Numerous granular processes | Consolidated into 34 practices |
| Focus | IT service management | Wider focus beyond IT to end-to-end service management |
| Guiding Principle | Lifecycle approach | Value driven approach |
| Key Publications | 5 core books for stages of service lifecycle | 1 core ITIL book and separate guidance books |
| Change Management | Separate process | Integrated across service value chain |
| Agility | Traditional planned approach | Built-in agility, DevOps, organizational change |
| Complexity | Complex to implement fully | Simplified implementation approach |
| Certifications | Multiple certifications for practitioners | 4 levels of certification for practitioners |
General Management Practices
Here is an overview of three key ITIL service strategy processes and general management practices:
1. Strategy Management
- Defines how IT services help achieve business objectives
- Analyzes internal and external factors that can influence strategy
- Formulates strategic plans and roadmaps for service development
- Maintains alignment between IT and business strategies
2. Service Portfolio Management
- Manages the end-to-end lifecycle of all services offered
- Maintains the Service Portfolio – a database of service details
- Categorises services, analyzes investment and ROI
- Ensures services enable business outcomes
3. Architecture Management
- Defines and maintains appropriate IT architectures
- Establishes standards and policies to guide technology decisions
- Ensures technical consistency and infrastructure efficiency
- Approves, maintains and governs IT architectures
These processes provide the strategy and planning foundation for IT service management. They guide strategic decision-making to build business-aligned IT services and architectures.
Service Management Practices
Here is an overview of some key ITIL service management practices:
Business Analysis
- Involves understanding the business vision, objectives, drivers, and needs
- Identifies how IT services can enable desired business outcomes
- Includes practices like strategy analysis, requirements definition, benchmarking
Service Catalogue Management
- Maintains a centralized repository of all active IT services
- Documents service details like features, status, costs etc.
- Ensures services are defined, available for use and meet needs
Service Design
- Designs new/changed services to meet business demands
- Includes designing processes, architectures, policies, documentation
- Ensures service design aligns to strategies and agreed levels
- Considers four design aspects – processes, architecture, measurement, technology
These practices transform strategic objectives into executable designs through detailed analysis, documentation and development. They enable the creation of business-aligned IT services built on robust process and technology foundations.
Technical Management Practices
Some of key technical management practices in ITIL are:
Deployment Management:
- Focuses on the deployment of new hardware, software, documentation etc. into live environments.
- Involves release planning, design of deployment infrastructure, rollout planning, testing and actual deployment.
- Ensures integrity of existing IT infrastructure while deploying changes.
- Uses techniques like piloting, staging, phased rollout etc. to mitigate risks.
- Maintains configuration baselines of infrastructure and applications.
Infrastructure and Platform Management:
- Manages the IT infrastructure like servers, networks, storage, databases etc. needed to develop, test, deliver, monitor and support IT services.
- Performs activities like infrastructure capacity planning, procurement, deployment, hardening, backups and restoration.
- Implements automation and tools for infrastructure provisioning, configuration and monitoring.
- Maintains optimal performance and availability of infrastructure platforms.
Software Development and Management:
- Covers the design, development, testing and maintenance of software applications.
- Follows software development lifecycle with phases like requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, release, maintenance.
- Adopts practices like version control, code review, automated testing and continuous integration.
- Leverages agile methods to enable rapid software delivery and accommodate changing needs.
- Ensures software quality, maintainability and alignment with IT service objectives.
Case Studies On ITIL Processes
Here are a couple of case studies demonstrating real-world applications and success stories of ITIL Processes:
Real-world Application: Large Financial Institution
A large financial institution implemented ITIL practices for IT service management. ITIL was used to redesign incident, problem, change, and release processes. This improved service desk efficiency by 20% and reduced downtime by 50% within the first year. ITIL implementation enabled the financial institution to provide consistent and high quality IT services.
Real-world Application: Government Agency
A government agency sought to improve its IT service quality. It adopted ITIL guidelines to establish well-defined incident management and service desk processes. As a result, incident resolution time was reduced significantly. ITIL implementation also improved knowledge transfer and boosted customer satisfaction through better service delivery.
Success Story: Multinational Software Company
A multinational software company was struggling with project delays and issues due to unmanaged changes. By implementing ITIL change management processes, they were able to assess, approve and track changes systematically. This resulted in a 30% reduction in unauthorized changes along with improved availability and reduced downtime. The ITIL framework implementation allowed the company to deliver IT changes more efficiently.
Success Story: Global Retail Enterprise
A global retail enterprise used ITIL’s continual service improvement methodology to overhaul its IT operations. ITIL CSIs enabled the organization to take a metrics-driven approach for improving services. This resulted in higher systems reliability, reduced costs, and alignment of IT to business goals. The enterprise was able to leverage ITIL to successfully transform its IT function.
ITIL Certification and Training
Here is an overview of ITIL certification and where you can get trained on ITIL processes:
ITIL Certification
ITIL has a tiered certification scheme that includes:
- ITIL Foundation – Entry-level certification covering ITIL basics
- ITIL Managing Professional (MP) – Intermediate certification for supervising ITIL practices
- ITIL Strategic Leader (SL) – Advanced certification for leadership/strategy
- ITIL Master – High-level certification for implementing ITIL lifecycle
These certifications demonstrate different levels of ITIL expertise and knowledge. They are globally recognised and sought after.
Where to Get ITIL Processes Training
There are several options to get trained on ITIL practices:
- Online Courses – Many accredited institutes like PeopleCert and Dion Training offer online ITIL courses and certification exam prep. This allows self-paced learning.
- In-person Training – Many organizations provide instructor-led ITIL training bootcamps to prepare for certification.
- ITIL Foundation Book – Axelos’ official ITIL 4 Foundation book covers processes in detail.
- ITIL Mobile App – Axelos’ free app contains ITIL study materials and glossary.
- Practice Exams – Taking sample tests from reputed practice exam providers tests knowledge.
A combination of self-study, formal training, and practice exams is recommended to master ITIL processes for certification and real-world application.
Future of ITIL : Upcoming Trends and Emerging Technologies
Here are some of the key upcoming trends and future directions for ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library):
- Greater focus on agile service management – ITIL will continue to evolve to support more agile and iterative approaches to IT service management. Frameworks like ITIL 4 have already incorporated agile concepts.
- Integration with DevOps – Increased collaboration between ITSM and DevOps teams is a major trend, as organizations aim to achieve faster delivery of IT services and meet changing business needs. ITIL practices will integrate more with DevOps tools and ways of working.
- Leveraging AI and automation – AI and intelligent automation will be utilized to streamline ITIL processes like incident management, problem management, change management etc. This can enable faster service delivery and improved efficiency.
- Adoption of cloud services – With the growth of cloud computing, ITIL will adapt to effectively manage cloud-based services, hybrid IT environments and service integration across on-premise and cloud.
- Internet of Things (IoT) support – The growth of IoT and connected devices across organizations will require ITSM practices like ITIL to manage and integrate these devices and data streams as part of IT services.
- Integration with other frameworks like SIAM – ITIL will intersect with other approaches like Service Integration and Management (SIAM) to enable coordination across multiple service providers.
- Focus on enhancing customer experience – ITIL will continue to evolve with more emphasis on delivering superior customer and user experiences across the service lifecycle.
ITIL will adapt and evolve to remain relevant for the rapid technological advancements happening across the IT landscape. The core ITIL principles and practices will be enhanced to address emerging trends.
Conclusion
ITIL provides a systematic approach to coordinating people, processes and technology for delivering quality IT services. ITIL processes cover the entire service lifecycle end-to-end. Adopting ITIL can help organisations enhance IT service quality, reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction. However, ITIL should be implemented in a flexible way tailored to an organisation’s unique needs. With proper adoption, ITIL processes can transform IT service management.
Try out our free resume checker service where our Industry Experts will help you by providing resume score based on the key criteria that recruiters and hiring managers are looking for.
References
Here are some good references related to ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library):
Books:
- “ITIL Foundation Handbook” by Axelos
- “ITIL 4 Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL 4 Foundation exam and beyond” by Claire Agutter and Helen Morris
- “ITIL For Dummies” by Peter Farenden
- “Passing Your ITIL Foundation Exam” by Liz Gallacher and Helen Morris
Websites:
- Axelos – The official publisher of ITIL content and accreditor of training organizations:
- AXELOS ITIL 4 Foundation Certification
- ITIL Official YouTube Channel – Video tutorials on ITIL
- BMC Blogs – ITIL section
Online Training:
- LinkedIn Learning ITIL Courses:
- Simplilearn ITIL Certification Training
These resources provide a good mix of training materials, official content, and expert guidance to learn about ITIL framework and best practices and ITIL processes
FAQs Related To ITIL
What is an ITIL process owner?
The process owner is responsible for ensuring that a particular ITIL process is carried out according to the agreed and documented procedures. They have the authority to make any changes needed to improve the process.
What are the modules in ITIL?
The key modules in ITIL 4 are ITIL Service Value System, Four Dimensions Model, Service Value Chain, ITIL Management Practices, and ITIL Guiding Principles.
What is the role of CMDB in ITIL?
The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is used to store and manage data about IT assets and configurations. It provides an accurate view of the IT infrastructure and services which aids many ITIL processes.
What is the role of ITSM?
IT Service Management refers to the implementation and management of quality IT services that meet business needs. ITIL provides best practice framework to implement ITSM across organisation.
What is difference between ITIL and ITSM?
ITIL is a set of best practices for IT service management outlined in a framework. ITSM refers to the broad practice and strategy of designing, delivering, managing and improving IT services. ITIL provides guidance on how to execute ITSM.