Table of Contents
ToggleIn this article we will discuss data hiding in Java which is an important concept in object-oriented programming. We will cover
- What is data hiding in Java
- How it is implemented in Java
- Differences between data hiding vs encapsulation and abstraction, and more through examples.
So let’s get started.
What is Data Hiding in Java?
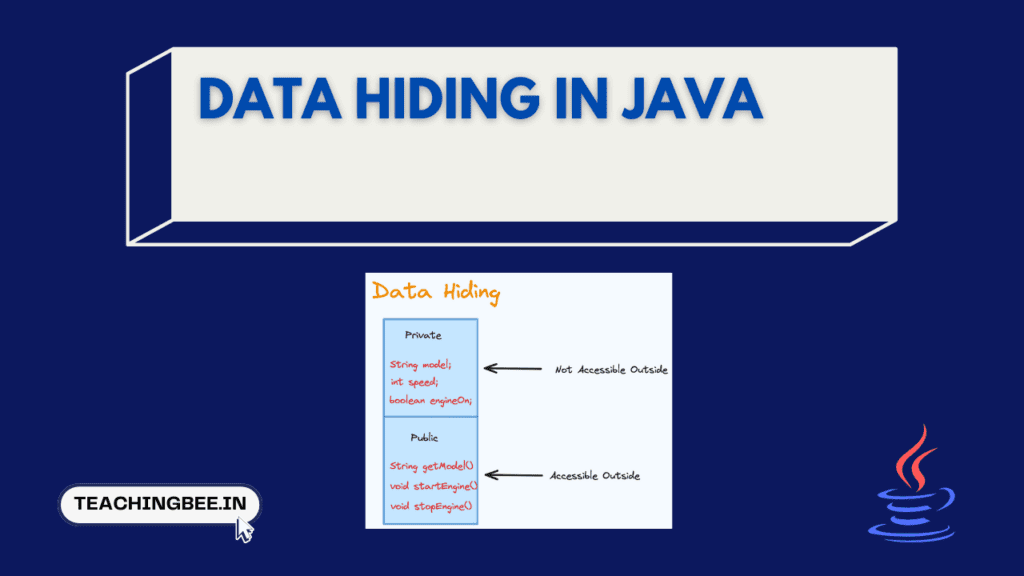
Data hiding in Java is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming (OOP). Data hiding in Java refers to the ability to prevent access to certain components inside an object in order to prevent unintended or unauthorised manipulation of data.
Think of a smartphone as an object in Java. It has various components inside like a processor, camera, battery etc. Now as an end user, you can use the external features of the phone – like taking pictures, playing games etc. But you cannot access the internal components directly – for example you cannot tamper with the processor or hardware directly. This is similar to data hiding in Java.
The phone manufacturer hides the implementation details and internal components from end users. This is similar to classes in Java using private and protected modifiers for variables and methods – to prevent direct access from outside the class. As an end user you can access certain public methods defined by the manufacturer but cannot directly access private components. This encapsulation and data hiding in java helps maintain integrity of data and prevent misuse or tampering.
So, just like smartphone manufacturers hide internal details of the phone from users, Java objects hide their private data and methods from other classes using access modifiers. This helps encapsulate and protect the data integrity and prevent unintended modifications – just like you cannot access the hardware inside a phone directly as an end user.
Implementing Data hiding In Java
Data hiding in Java can be implemented using private access modifiers for the class’s fields (variables) and providing public methods (often getters and setters) to access and modify these fields. This is a part of the broader concept of encapsulation. Let’s consider an example to illustrate this:
Example: A Person Class
public class Person {
// Private fields: Data hiding in action
private String name;
private int age;
// Constructor to initialize fields
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// Public getter for name
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// Public setter for name
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// Public getter for age
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
// Public setter for age
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age > 0) { // Simple validation
this.age = age;
}
}
}In this example:
- Private Fields: The
nameandagefields are declared asprivate. This means they cannot be directly accessed from outside thePersonclass. This is data hiding in java. - Public Methods (Getters and Setters): The
getName,setName,getAge, andsetAgemethods are public. These methods provide a controlled way to access and modify the private fields. For instance,setAgeincludes a simple check to ensure that the age is positive before setting it. - Using the Class:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("Alice", 30);
// Accessing data through public methods
System.out.println("Name: " + person.getName());
System.out.println("Age: " + person.getAge());
// Modifying data through public methods
person.setAge(31);
person.setName("Alice Smith");
// Again accessing data through public methods
System.out.println("Updated Name: " + person.getName());
System.out.println("Updated Age: " + person.getAge());
}
}In the Main class:
- The
Personobject is created with initial values. - The private data (
nameandage) of thePersonobject is accessed and modified using the public methods. - Direct access to the
nameandagefields is not possible from outside thePersonclass, which demonstrates data hiding in java.
This approach allows you to hide the internal representation of an object and expose only what is necessary, providing a clear interface for interaction while maintaining the integrity and security of the internal state of the object.
Access Specifiers In Java
| Access Modifier | Class Level | Package Level | Subclass (Same Package) | Subclass (Different Package) | Global |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
public | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
protected | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (Through Inheritance) | No |
default (no modifier) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
private | Yes | No | No | No | No |
For more detailed explanation read our previous post private and protected modifiers.
Encapsulation Vs Data Hiding in Java
Encapsulation and Data Hiding are two fundamental concepts in object-oriented programming, especially in Java. They are often used together, but they have distinct meanings:
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is the technique of bundling the data (variables) and the methods that operate on the data into a single unit or class. It also controls access to that data. The main purpose of encapsulation is to protect the data from outside interference and misuse.
Data Hiding
Data hiding in java, a subset of encapsulation, is the principle of restricting access to the internal state or the data of an object. This is generally achieved by making the variables of a class private and providing public methods to access and modify them.
Java Code Example
Consider a simple Car class to illustrate both concepts:
public class Car {
// Data Hiding: The internal state of the car is private
private String model;
private int speed;
private boolean engineOn;
// Constructor encapsulating the initial setup
public Car(String model) {
this.model = model;
this.speed = 0;
this.engineOn = false;
}
// Public method to encapsulate the logic of starting a car
public void startEngine() {
if (!engineOn) {
engineOn = true;
System.out.println(model + " engine started.");
}
}
// Public method to encapsulate the logic of stopping a car
public void stopEngine() {
if (engineOn) {
engineOn = false;
speed = 0; // Resetting speed to 0 when engine is off
System.out.println(model + " engine stopped.");
}
}
// Getter method for model, demonstrating data hiding
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
// Public method to increase speed, encapsulating the logic
public void accelerate(int increment) {
if (engineOn) {
speed += increment;
System.out.println(model + " speed increased to " + speed + " km/h.");
}
}
}In this example:
- Data Hiding: The
model,speed, andengineOnfields are private. This means they cannot be accessed directly from outside theCarclass, effectively hiding the data. - Encapsulation: The methods
startEngine,stopEngine,getModel, andaccelerateprovide a controlled way to interact with theCarobject. They encapsulate the logic for operating on the car’s data. For example, theacceleratemethod increases the speed only if the engine is on, encapsulating this logic within the method.
In Short,
- Data Hiding in Java is about making the data of a class private to prevent direct access.
- Encapsulation involves bundling data and methods together and providing a controlled interface for interacting with that data (e.g., public methods to start/stop the engine, accelerate, etc.).
Both concepts work together to improve the robustness, maintainability, and security of the code.
Abstraction Vs Data Hiding in Java
Abstraction, is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming, is about hiding the complex implementation details and showing only the necessary features of an object. It allows the programmer to focus on what an object does, rather than how it does it. This is typically achieved through abstract classes and interfaces in Java.
Java Code Example
Implementing Data Hiding In Java
public class BankAccount {
// Data hiding: Private internal state
private double balance;
public BankAccount(double initialBalance) {
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
// Public methods to access and modify the private balance
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
balance += amount;
}
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount > 0 && balance >= amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}Implementing Abstraction
public abstract class Vehicle {
// Abstract method
public abstract void startEngine();
// Another abstract method
public abstract void stopEngine();
}
public class Car extends Vehicle {
@Override
public void startEngine() {
// Implementation for starting a car's engine
System.out.println("Car engine started.");
}
@Override
public void stopEngine() {
// Implementation for stopping a car's engine
System.out.println("Car engine stopped.");
}
}In the BankAccount class, data hiding in java is demonstrated by making the balance variable private and controlling its access through public methods like deposit, withdraw, and getBalance.
In the Vehicle and Car classes, abstraction is shown by defining a general Vehicle class with abstract methods like startEngine and stopEngine. The Car class, which extends Vehicle, provides specific implementations for these methods. This abstraction allows users of the Car class to simply know that they can start and stop the engine, without needing to know the underlying implementation details.
So,
- Data Hiding in Java is concerned with protecting the internal state of an object by making it inaccessible from outside the object’s methods.
- Abstraction focuses on hiding the complexity of implementation and exposing only the necessary functionality to the user.
| Aspect | Encapsulation | Data Hiding | Abstraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bundling of data with the methods that operate on that data. It also involves controlling the access to that data. | Specifically the practice of keeping the internal data of a class hidden from external access. | The concept of hiding the complex reality while exposing only the necessary parts. It’s about showing only essential features and hiding the details. |
| Implementation in Java | Achieved using classes, where data members and methods are combined. Access modifiers control the visibility. | Generally implemented by declaring class members as private and providing public getter/setter methods. | Implemented using abstract classes and interfaces. Abstract methods define ‘what’ a class can do, without specifying ‘how’. |
| Primary Objective | To protect an object’s integrity by preventing unauthorized parties from tampering with its internal processes. | To protect the inner workings of an object from being exposed to the outside. | To simplify complex reality by modeling classes focused on relevant operations, hiding unnecessary details. |
| Focus | On how data is accessed and modified. | On restricting access to internal data. | On the interface/exposed functionality, rather than the implementation details. |
| Example | A class Car with private fields and public methods to operate on those fields. | A class with private fields (e.g., private int speed;) and no direct access from outside the class. | An interface Vehicle with methods like start() and stop(), but without implementation details. |
Key TakeAways
- Data hiding in Java refers to making the fields in a class private to prevent direct access from outside the class. Getter and setter methods can be used to access and modify private fields indirectly.
- Data hiding helps protect sensitive data from unintended or unauthorized access and provides greater control over how data is accessed or modified.
- Encapsulation refers to bundling data and methods into a single unit or object. Data hiding is a specific part of encapsulation related to keeping fields private.
- Abstraction focuses on simplifying complex implementations by modeling classes around key operations. Data hiding specifically deals with restricting access to fields representing internal state.
- By using access modifiers like private and protected, Java enables data hiding, a key principle for secure and maintainable object-oriented design.
Checkout more Java Tutorials here.
I hope You liked the post 👍. For more such posts, 📫 subscribe to our newsletter. Try out our free resume checker service where our Industry Experts will help you by providing resume score based on the key criteria that recruiters and hiring managers are looking for.
FAQ
What is the data hiding method?
Data hiding is an object oriented programming concept that involves making the fields within a class private to prevent direct access to them from code outside the class. It is done to protect sensitive data from unintended modification.
What is known as hiding of data?
Hiding of data refers to making the data members or fields of a class private by using Java’s private access modifier. This restricts direct access to those fields from external code.
How can we hide the data in Java?
In Java, data hiding is accomplished by declaring fields/variables as private within the class. This stops external code from directly accessing those fields. To allow accessing private fields in a controlled way, public getter and setter methods are provided which allow retrieving or modifying the value of private fields.