Table of Contents
ToggleIn this article, we will see how to check a given year is leap year or not in Java. We will also see various ways to implement Leap Year Program In Java. So,
Let’s dive in.
Problem Statement
Write a Java program to determine whether a given year is a leap year or not.
For Example:
Input: 2024
Output: Leap Year
Input: 1900
Output: Not a Leap YearSolution
Before proceeding to solution let’s see what actually is a leap year.
What is a Leap Year?
A leap year is a year that contains an extra day, i.e. 366 days in the calendar, whereas a regular or non-leap year has 365 days.
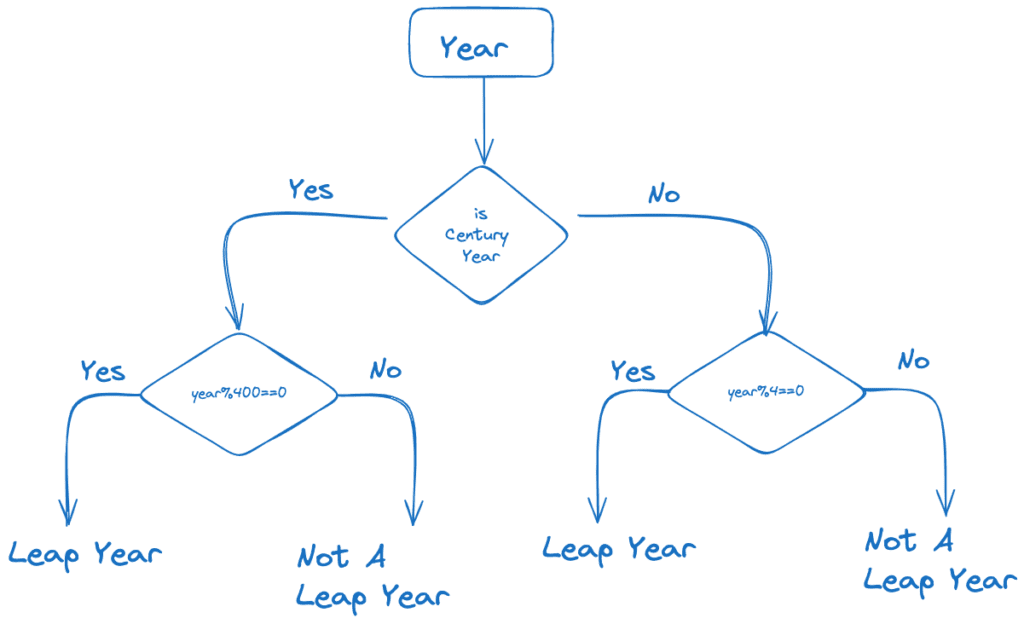

Rules To Check if Given Year is Leap Year Or Not
- A year is a leap year if it is exactly divisible by 4.
- If the year is century year (a year ending with 00), then it is a leap year only if it is divisible by 400.
- So, A century year should be divisible by 4 and 100 both.
- A non-century year should be divisible only by 4.
We will see three different ways to check if given year is leap year or not. Those are:
- Using if-else
- Using Ternary Operators
- Using In-built isLeap() Method
Approach 1: Using if-else
Let’s check how to check if given year is leap year or not in java using if-else
Algorithm
- Given the input year (
year) that you want to check. - Check if it’s a century year (ends with 00):
- Use the modulo operator
%to check ifyear % 100== 0.
- Use the modulo operator
- If it’s a century year, check if it’s divisible by 400:
- Use the modulo operator
%to check ifyear % 400== 0.
- Use the modulo operator
- If it’s not a century year, check if it’s divisible by 4:
- Use the modulo operator
%to check ifyear % 4== 0.
- Use the modulo operator
- If it’s a century year and divisible by 400, it’s a leap year.
- If it’s not a century year and divisible by 4, it’s a leap year.
- If it’s a century year but not divisible by 400, it’s not a leap year.
Java Program To Check Leap Year Using if-else
// Leap Year Program In Java Using if-else
public class LeapYearChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2024; // Replace this with the year you want to check
// Check if it's a century year (ends with 00)
if (year % 100 == 0) {
// If it's a century year, check if it's divisible by 400
if (year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + " is a Leap Year");
} else {
// If it's a century year but not divisible by 400, it's not a leap year
System.out.println(year + " is not a Leap Year");
}
} else {
// If it's not a century year, check if it's divisible by 4
if (year % 4 == 0) {
// If it's not a century year but divisible by 4, it's a leap year
System.out.println(year + " is a Leap Year");
} else {
// If it's not a century year and not divisible by 4, it's not a leap year
System.out.println(year + " is not a Leap Year");
}
}
}
}
Output
2024 is a Leap YearCode Explanation
- Check if it’s a century year (ends with 00):
2024 % 100==24, so it’s not a century year.
- Since it’s not a century year, check if it’s divisible by 4:
2024 % 4==0, so it’s divisible by 4.
- As it’s not a century year but divisible by 4, so it’s considered a leap year.
Approach 2: Using Ternary Operator
Let’s optimise the above code to single line using ternary operator.
Algorithm
- Given the input year (
year) that you want to check. - Use the ternary operator
? :to perform the leap year check in a single line. - Check if it’s a century year (ends with 00):
- Use the modulo operator
%to check ifyear % 100is equal to 0.
- Use the modulo operator
- If it’s a century year, check if it’s divisible by 400 using the ternary operator:
(year % 400 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year"
- If it’s not a century year, check if it’s divisible by 4 using the ternary operator:
(year % 4 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year"
- The ternary operator will return either “Leap Year” or “Not a Leap Year” based on the conditions.
Java Program To Check Leap Year Using Ternary Operator
// Leap Year Program In Java Using if-else
public class LeapYearChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2024; // Replace this with the year you want to check
// Use the ternary operator to check if it's a leap year
String result = (year % 100 == 0) ? (year % 400 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year" : (year % 4 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year";
System.out.println(year + " is " + result);
}
}
Output
2024 is Leap YearApproach 3: Using In-built isLeap() Method
Java java.time.Year class in the Java Date and Time API provides an isLeap() method to check if a year is a leap year.
Algorithm
- Given the input year (
year) that you want to check. - Create a
java.time.Yearobject using the input year. - Use the
isLeap()method to check if it’s a leap year:Year.isLeap(year)
- The method will return
trueif it’s a leap year andfalseotherwise.
Java Program To Check Leap Year Using In-built isLeap() Method
// Leap Year Program In Java Using In-built isLeap() Method
import java.time.Year;
public class LeapYearChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2024; // Replace this with the year you want to check
// Create a Year object and use isLeap() method
boolean isLeapYear = Year.of(year).isLeap();
if (isLeapYear) {
System.out.println(year + " is a Leap Year");
} else {
System.out.println(year + " is not a Leap Year");
}
}
}Output
2024 is a Leap YearLeap Year Program In Java Using Scanner
In all the above code the input year was hard coded. Now, let’s take this input from user via Scanner.
// Leap Year Program In Java Using Scanner
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner object for user input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a year: ");
int year = scanner.nextInt(); // Read the input year from the user
// Close the Scanner to avoid resource leaks
scanner.close();
// Use the ternary operator to check if it's a leap year
String result = (year % 100 == 0) ? (year % 400 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year" : (year % 4 == 0) ? "Leap Year" : "Not a Leap Year";
System.out.println(year + " is " + result);
}
}Similarly all the other above methods discussed can be converted to take input from user using Scanner library.
Output
Enter a year: (user enters the year, e.g., 2024)
2024 is Leap YearKey Takeaways
- A year is a leap year if it is divisible by 4 but not by 100, or if it is divisible by 400. This is the logic used to determine if a year is a leap year.
- Using if-else statements, we can check for century year, divisibility by 4 and 400 to implement the leap year logic.
- Ternary operator can be used to condense the if-else logic into a one-liner expression using modulo and conditional operators.
- Java’s inbuilt Year class provides an isLeap() method to easily check if a year is a leap year without manual logic.
Similar Posts
Add Days To The Current Date in Java
Calculate Area of Hexagon in Java
Program to Calculate EMI in Java
Calculate Area of a Circle in Java
Checkout more Java Tutorials here.
I hope You liked the post ?. For more such posts, ? subscribe to our newsletter. Try out our free resume checker service where our Industry Experts will help you by providing resume score based on the key criteria that recruiters and hiring managers are looking for.
FAQ
What are the advantages of using Java’s inbuilt isLeap() method?
The inbuilt isLeap() method provides a simple and cleaner way to check for leap year. It handles all the logic internally and we don’t have to write the logic manually. Also, it would be more robust and efficient being part of standard library.
How to check leap year for user input year in Java?
You can take year input from user via Scanner or console. Parse the input to int using Integer.parseInt(). Pass this year to isLeap() method or use it in your manual logic to determine if that particular year is a leap year or not. Display the result.
What are the leap years between 1990 to 2022?
1992, 1996, 2000, 2004, 2008, 2012, 2016, 2020 are leap years between 1990 to 2022.
Why are leap years needed?
Leap years sync the calendar year with astronomical year preventing mismatch over time. It maintains correspondence of calendar months with seasons.