Table of Contents
ToggleMenu driven program in java are a useful technique in Java for building interactive applications that provide multiple options to the user. The program displays a menu and performs different operations based on the user’s choices.In this article, we covered several aspects of menu driven programs:
- What are menu driven program in java?
- Basics of Switch Case in Java.
- Menu Driven Program Examples.
- Discussing if-else as alternative.
Menu Driven Programs in Java
A menu driven program displays a menu of options to the user and performs different operations based on the user’s choice.
- It allows the user to choose what operation they want to execute through the menu.
- The menu is displayed in a loop so that the user can perform multiple operations repeatedly.
- Switch case is commonly used to implement the logic to execute different operations based on menu choice.
For example, a basic menu driven calculator program may display:
1. Addition
2. Subtraction
3. Multiplication
4. Division
5. ExitAnd perform the chosen arithmetic operation based on the user’s input.
Menu driven programs allow flexible, interactive execution of multiple options within a single program.
Switch Case in Java
The switch case statement routes program execution to different blocks of code based on a control expression.
// Switch Case Statement In Java
switch(expression) {
case value1:
// code block 1
break;
case value2:
// code block 2
break;
default:
// default block
}- The switch expression is evaluated and compared to the case values.
- When a match is found, execution jumps to that case block.
- The break statements exit the switch block after a case executes.
- The default case runs if no match is found.
Switch case provides an easy way to implement conditional logic that chooses between multiple code paths. It is very useful in menu driven programs for routing to the chosen menu option’s operation.
Switch Case Java Program
Here is a simple program that demonstrates switch case usage:
// Switch Case Java Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int choice = 2;
switch(choice) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Choice is 1");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Choice is 2");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid choice");
}
}
}Output
Choice is 2The switch case compares choice and executes the matching case block. This routes code execution based on user input.
Now let’s look into how do we build a menu driven program in Java.
Algorithm for a Menu-driven Program
Menu Driven Program follows below template and steps:
- Program generally starts by displaying a menu of options.
- Continuously take and process user’s choices until they decide to stop.
- For each valid choice, perform the corresponding operation or execute a default action.
- Allow the user to continue or exit the program based on their preference.
So the algorithm of menu driven programs goes like this:
1. Start
2. Display menu options
3. Read user's choice input
4. While valid choice is entered:
4a. If choice is 1:
Perform Operation 1
4b. If choice is 2:
Perform Operation 2
4c. If choice is 3:
Perform Operation 3
4d. If choice is 4:
Perform Operation 4
4e. Else:
Perform Default Operation
5. Ask user if they want to continue
6. If user wants to continue, go to step 2
7. Else, stop program
Menu Driven Program In Java Examples
Now, let’s see examples and apply this algorithm in that example.
Menu Driven Calculator Program In Java Using Switch Case
Problem Statement
Write a program to perform arithmetic operations using switch case. The program should:
- Display a menu with options for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exiting.
- Continuously take user input and perform the chosen arithmetic operation on two numbers.
- Handle division by zero gracefully.
- Provide feedback for invalid choices.
- Allow the user to exit the program.
Solution
Let’s apply above algorithm in this Menu Driven Calculator problem.
- We will start program by displaying menu options that are basic arthemitic operatiosn addition, subtraction, multiplication, division which will be under infinite while loop
- User input is taken using Scanner Library
- Decision based on user’s input is made using switch case.
- Each case performs a specific arithmetic operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division), handles input, and displays the result.
- The program can be exited gracefully by selecting option 5, which closes the
Scannerand exits the program.
Arithmetic Operations Using Switch Case In Java
Let’s see java program for addition subtraction multiplication division arithmetic operations.
// Arithmetic Operations Using Switch Case In Java
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Continuous menu loop (Infinite Loop)
while (true) {
System.out.println("Calculator Menu");
System.out.println("1. Addition");
System.out.println("2. Subtraction");
System.out.println("3. Multiplication");
System.out.println("4. Division");
System.out.println("5. Exit");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int choice = sc.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
// Perform Addition operation
System.out.print("Enter two numbers: ");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
int sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
break;
case 2:
// Perform Subtraction operation
System.out.print("Enter two numbers: ");
int num3 = sc.nextInt();
int num4 = sc.nextInt();
int difference = num3 - num4;
System.out.println("Difference = " + difference);
break;
case 3:
// Perform Multiplication operation
System.out.print("Enter two numbers: ");
int num5 = sc.nextInt();
int num6 = sc.nextInt();
int product = num5 * num6;
System.out.println("Product = " + product);
break;
case 4:
// Perform Division operation
System.out.print("Enter two numbers: ");
double num7 = sc.nextDouble();
double num8 = sc.nextDouble();
if (num8 == 0) {
System.out.println("Error: Division by zero");
} else {
double quotient = num7 / num8;
System.out.println("Quotient = " + quotient);
}
break;
case 5:
// Exit the program
System.out.println("Exiting the calculator. Goodbye!");
sc.close();
System.exit(0);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid choice");
}
}
}
}Output
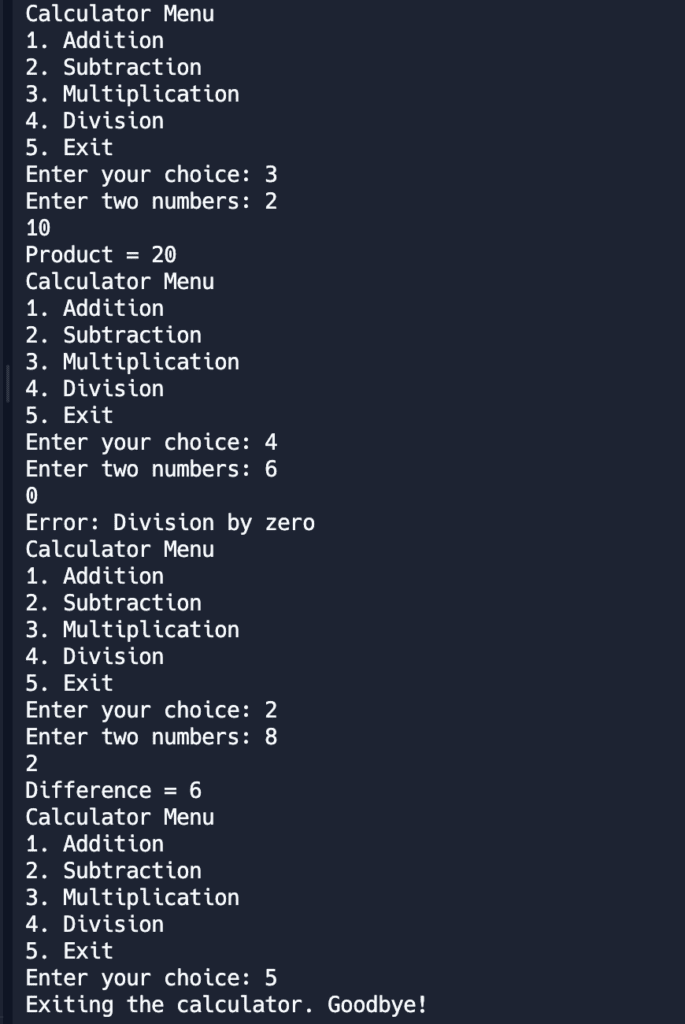

Let’s discuss alternatives for handling menu-driven options in Java without using a switch statement by using if-else statements .
Menu Driven Banking Program In Java Using if else
In this approach, we’ll use a series of if-else statements to check the user’s choice and execute the corresponding code block for each option.
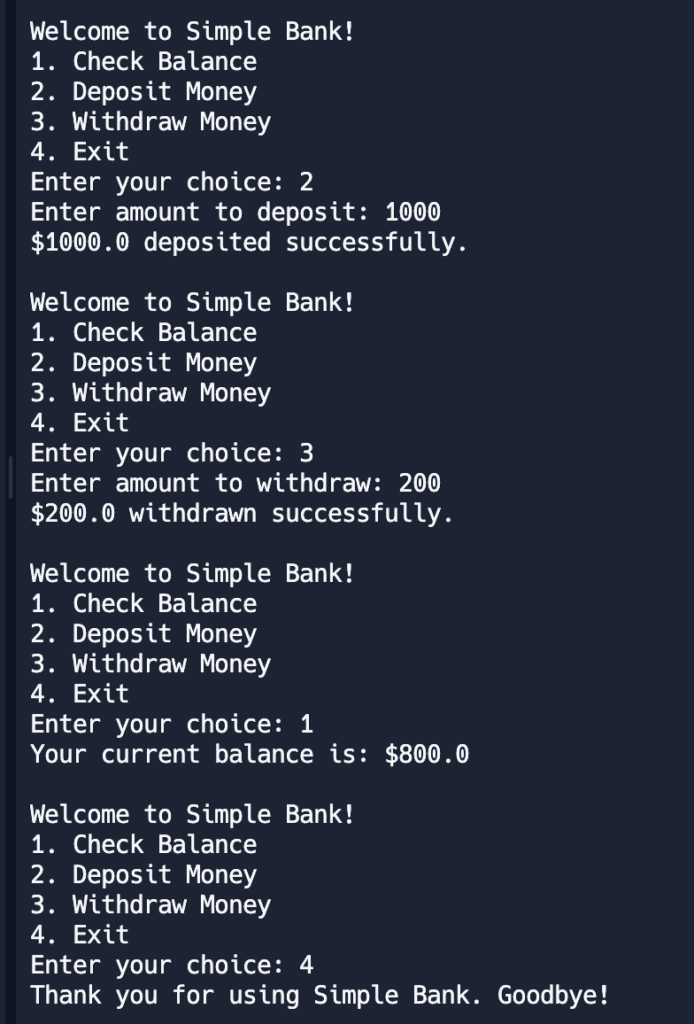
Let’s consider a real-world example of a menu-driven program in Java using if-else statements. In this example, we’ll create a simple banking application where a user can check their balance, deposit money, and withdraw money. For simplicity, we won’t implement actual banking logic but will focus on the structure of a menu-driven program.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BankingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double balance = 0.0;
while (true) {
// Display the menu
System.out.println("\nWelcome to Simple Bank!");
System.out.println("1. Check Balance");
System.out.println("2. Deposit Money");
System.out.println("3. Withdraw Money");
System.out.println("4. Exit");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
// Get user input
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
// Process the choice
if (choice == 1) {
// Check Balance
System.out.println("Your current balance is: $" + balance);
} else if (choice == 2) {
// Deposit Money
System.out.print("Enter amount to deposit: ");
double amount = scanner.nextDouble();
if (amount > 0) {
balance += amount;
System.out.println("$" + amount + " deposited successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid amount.");
}
} else if (choice == 3) {
// Withdraw Money
System.out.print("Enter amount to withdraw: ");
double amount = scanner.nextDouble();
if (amount > 0 && amount <= balance) {
balance -= amount;
System.out.println("$" + amount + " withdrawn successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid amount or insufficient funds.");
}
} else if (choice == 4) {
// Exit
System.out.println("Thank you for using Simple Bank. Goodbye!");
break;
} else {
// Invalid Choice
System.out.println("Invalid choice. Please try again.");
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
Output

How to Exit from a Menu-Driven Program
You can terminate a menu-driven program by incorporating a specific case in the switch statement to invoke the System.exit(int) method. This method is used to stop the currently running Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It requires a status code as an argument, which is used to indicate the termination status of the program. This approach is effective for gracefully exiting a program and signaling its completion status to the system.
Key Takeaways
- Menu driven programs allow the user to choose operations through a menu
- Switch case is commonly used to route between menu options
- Each case contains logic to perform the selected operation
- Validating input and looping allows repeated use
- Alternatives like if-else can also implement menus
- Menu driven structure enables interactive, flexible programs
Checkout more Java Tutorials here.
I hope You liked the post ?. For more such posts, ? subscribe to our newsletter. Try out our free resume checker service where our Industry Experts will help you by providing resume score based on the key criteria that recruiters and hiring managers are looking for.
FAQ
What is the use of menu driven program?
Here are some of the main uses and benefits of menu driven programs:
- User Interactivity – Menu driven programs allow the user to directly interact with the application by choosing options. This provides a user-friendly interface.
- Flexibility – The menu structure makes it easy to add, remove or modify options without having to restructure the core program logic.
- Code Reuse – Common functionality like input validation can be reused across menu options instead of rewritten.
- Separation of Concerns – Each menu option can be handled in its own modular block of code, separating concerns.
- Simplified Navigation – Menus make it easy for users to understand available actions and navigate the program.
How to create a menu menu in Java?
To create a menu in Java:
- Use a loop (like a while or do-while loop) to display the menu options and prompt the user to make a selection.
- Use a switch statement to execute different code blocks based on the user’s menu selection.
- You can store the menu options in an array or ArrayList and loop through them to display each option.
- Use Scanner to get the user’s menu choice as an int or String.
- After each menu option is executed, display the menu again until the user chooses to exit.
What is menu driven in data structure?
A menu-driven program in data structures is one where the user is presented with a menu of operations they can perform on a data structure (like stack, queue, tree etc). Based on the user’s menu choice, the appropriate data structure operation is executed.
For example, for a stack, the menu could allow pushing, popping, peeking, checking empty etc. For a queue, the menu could allow enqueue, dequeue, peek, check empty etc.